What is Porter’s Five Forces Model
Porter’s Five Forces Model is a qualitative way for analyzing a company and studying its business model in order to understand its position of the business in the market.
It is also a mode for setting a valuation for a startup in the early stage when the fundamental numbers may be weak.
Porter’s five forces are divided into 3 horizontal and 2 vertical categories
Horizontal forces
- Threat of new entrants
- Threat of substitutes
- Industrial rivalry
Vertical forces
- Bargaining power of suppliers
- Bargaining power of buyers
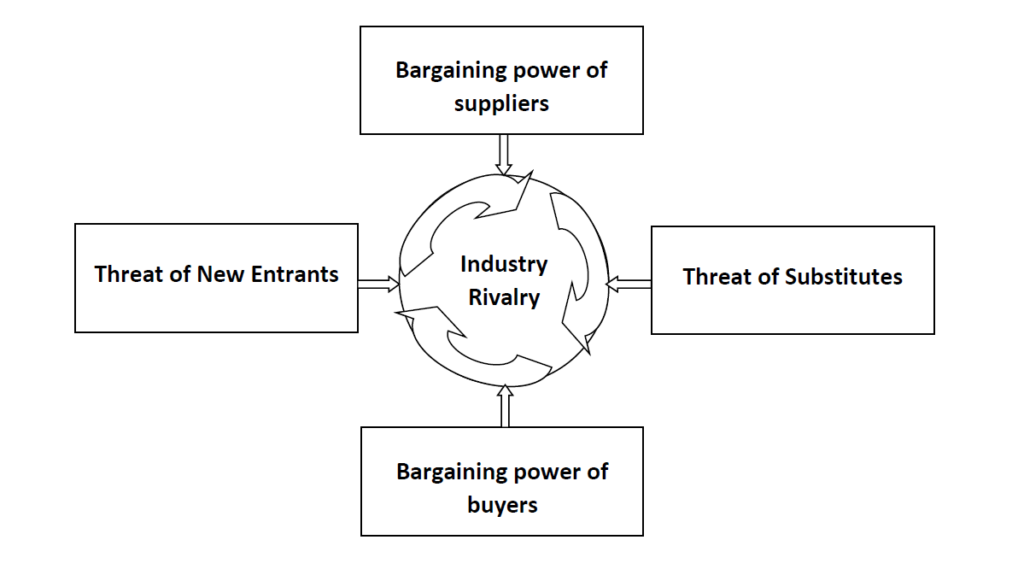
Porter’s Five Forces Model
Horizontal forces
Threat of new entrants
Threat of new entrants is defined as the complexity that a new entity will face when entering the business. This complexity can be in the form of extensive capital requirement, licenses and certificates, skills and software etc.
A startup that does not face the danger of new rivals would be appealing to investors and business owners.
If a business model has low entry barriers, it will be easily copied by the competition. This can result in market dilution and the business may not be able to meet the desired customers in order to sustain.
For example, Zerodha is a brokerage company. It provides services to allow investor to buy / sell shares from the stock exchange. Since there are already a large number of entry barriers in the form of SEBI regulations, licenses and technology requirement, the threat by new entrants becomes relatively low.
Threat of substitutes
Threat of substitution can be regarded as a tendency for a product / services be replaced by another product / services.
Substitution of a product can arise due to the shift in the habits of the consumer.
A large influencer for changing habits can be the use of technology. The startups need to be updated to technology at all times to stay relevant to their consumers.
A classic example of this is how the digital camera in today’s generation have completely replaced the traditional film camera. Had Kodak tried to stay relevant with the change in technology, it would not need to file for bankruptcy.
An investor needs to check whether the product / services they are investing do not have any probable threat for substitution in the future. If yes, then how does the management of the startup are prepared to adapt to this change.
Industrial rivalry
Industrial rivalry is the competition between the current market participants in the business sector. These businesses are in a constant battle between to provide their best services at all times and prove to be better than their competition.
A good competition can be healthy for the companies to grow and maintain their best services at all times. But there can be instances where one company can completely over take the other.
When competition is fierce, the ultimate effect is weaker pricing power and lower earnings for industry players. In this market, product innovation as well as customer service and engagement activities become critical.
A powerful rival with substantial funds may readily use strategies like constantly dumping products / services at rates below cost to push others out of the business.
For examples, an industrial rivalry between Swiggy and Zomato. These both food deliver platforms needs to constantly provide the best services, improve with technology and keep their customers happy in order to stay in business.
It is to be noted that, the industrial rivalry can also act like a strong entry barrier for new players to enter the sector.
Vertical forces
Bargaining power of suppliers
This is a scenario where products / services of a particular startup are not actively available in the market and not able to meeting the increasing demand.
This gives an opportunity to the companies to quote the rates as per their choice and have higher profit margins. The supplier is in control of the price of the product.
Lesser products / services available in the market make the businesses have higher profit margins.
For example, the prices of medicines or medical fees are not in the control of the buyer. The consumer needs to pay the money regardless of the prices quoted by the doctor. On the other hand, at a vegetable outlet, the consumer is in control of the price and the seller has to adjust his prices as per the buyers demand.
Bargaining power of buyers
If there are several companies offering identical products / services, buyers may exert a lot of pressure and influence prices. On the other hand, if there are few industries for a product / service, they may not have as much effect.
In a nutshell, it’s a function of the quantity of buyers and sellers, as well as the differences in their products / services, that might influence buyers negotiating power in a given sector.
The customer size and prominence, like a the government or a larger corporate as a buyer of a product or service, might also impact their negotiating power.
Conclusion
Understanding all the five pillars of Porter’s Five Forces Model is extremely important while analyzing a company. This model will showcase the true picture of the business and help in predicting the future for the startup.
Also Read: How To Value Stocks Using Sum Of The Parts (SOTP) Valuation Model

